Long before NAFEMS and other organizations began to promote it as a Big Issue, ESRD and its partners coined the term “Simulation Governance” to describe the proper implementation of numerical simulation. Since 1989, ESRD’s implementation of FEA was inherently designed to satisfy the requirements of Simulation Governance, making ESRD a trailblazer in this topic.
Simulation Governance
Want to schedule a Simulation Governance briefing?
Would you like to learn more about how Simulation Governance can be implemented for your organization? Complete the form and we will follow up shortly.

Simulation Governance is an open-ended process by which mathematical models are ranked and progressively improved over time in the light of new experimental data. The following sheds more light on this process, as well as its importance, technical requirements and helpful resources.
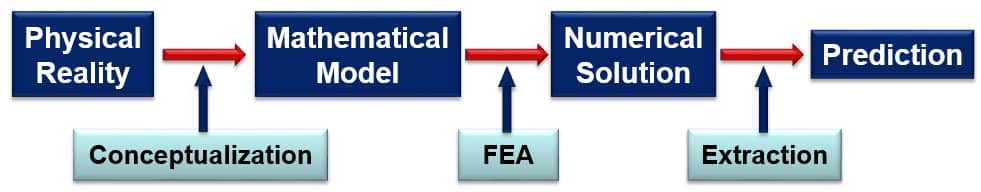
Simulation governance is a managerial function concerned with assurance of reliability of information generated by numerical simulation through:
- The selection and adoption of the best available simulation technology,
- Assurance that mathematical models have been properly formulated and validated,
- Establishment of data and solution verification procedures,
- Management of experimental data,
- Revision of mathematical models in the light of new information collected from physical experiments and field observations.
Simulation Governance is formally defined in Wikipedia:
Simulation governance is concerned with (a) selection and adoption of the best available simulation technology, (b) formulation of mathematical models, (c) management of experimental data, (d) data and solution verification procedures, and (e) revision of mathematical models in the light of new information collected from physical experiments and field observations [4].
A plan for simulation governance has to be tailored to fit the mission of each organization or department within an organization: If that mission is to apply established rules of design and certification then emphasis is on solution verification and standardization. If, on the other hand, that mission is to formulate design rules, or make condition-based maintenance decisions, then verification, validation and uncertainty quantification must be part of the plan.

We take V&V and Simulation Governance seriously.
In 2012, Drs. Barna Szabo and Ricardo Actis of ESRD, Inc. published the first known document detailing simulation governance. This was titled ‘Simulation governance: Technical requirements for mechanical design’, and was published in Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 249-252 (2012) 158-168.
The term simulation governance refers to procedures established for the purposes of ensuring and enhancing the reliability of predictions based on numerical simulation.
ESRD’s Chairman and Co-Founder, Dr. Barna Szabó, explains how Sim Gov came to be:
As recorded at the 30th International CAE Conference in Verona, Italy
ESRD leads the forefront of the development and implementation of Sim Gov in modern numerical simulation products, including StressCheck Professional, CAE Handbook, StressCheck Tool Box and its consulting solutions.
Management is responsible for command and control of numerical simulation, so management is responsible for simulation governance.

All major industrial organizations employ numerical simulation in support of their engineering and business decision-making. Therefore using or not using numerical simulation is no longer a differentiator.
The differentiator is: How smartly numerical simulation is being used? Depending on the answer, numerical simulation can be a significant corporate asset or a substantial corporate liability.
Whenever engineering or business decisions are based on the results of numerical simulation there is an implied expectation of reliability. Without such expectation it would not be possible to justify the time and cost of a simulation project. In fact, if simulation produces misleading information then it has a negative economic value.
There are many well-documented cases of expensive repairs, retrofits, project delays and serious safety issues arising from lack of simulation governance. The practice of simulation governance becomes critical for ensuring the reliability and robustness of analysis methods and tools used in support of engineering decision-making processes.
The standardization, automation, and democratization of new technologies such as Sim Apps through the adherence to the practice of Simulation Governance offers many benefits to industry at the engineering, product, and business levels. These benefits include encapsulating complexity, improving productivity, containing cost, and ensuring reliability for the expert simulation analyst and non-expert design engineer alike.

As the value of the simulation function increases the practice of simulation governance becomes critical to ensuring the reliability and robustness of analysis methods and tools used in support of engineering decision-making processes.
Below is a snapshot of quotes from engineering simulation thought leaders and Simulation Governance experts:
The finite element method is used by engineers daily in the design/assessment of components and structures. The number of engineers using such tools is increasing and will increase further with the so-called democratisation of simulation. However, whilst the method might appear easy to use, with highly effective graphical user interfaces, the fundamental fact is that it is approximate and can produce significant errors in the hands of the inexperienced engineer. These errors, if undetected, can compromise a design to such an extent that it becomes unfit for purpose or, even, unsafe. The way to avoid such finite element malpractice is through the application of sound simulation governance.
Dr. Angus Ramsay
Engineering/Managing Director, Ramsay-Maunder Associates…given compressed development schedules, it is hard to obtain representative parts (built on production tooling) in sufficient time to then test them and make engineering decisions. Also, it is prohibitively expensive to do statistically valid physical testing.
So, for that reason, companies need to look at how they manage their simulation strategy, what we call Simulation Governance. This is an issue for senior executive management, not just the high priests of simulation.
Dr. Keith Meintjes
Executive Consultant, CIMDataHaving a simulation capability is no longer a differentiator. To remain competitive companies need to have a capability and be able to use the capability effectively to produce results that are reliable and repeatable. Generating confidence in the capability of the simulation team is essential to move analysis from being a ‘tick box’ in the design process to a strategic capability
Dr. Althea de Souza
Director, Quesada SolutionsDespite recognition of the importance of simulation, there is not much short term prioritisation from businesses for V&V improvements. As a result, we must consider how to strengthen managers’ awareness for V&V and credibility assurance
Jean-François Imbert
NAFEMS TutorSimulation governance is concerned with the selection and adoption of the best available simulation technology, the formulation of mathematical models, the management of experimental data, the verification procedures, and the revision of mathematical models in the light of new information collected from physical experiments and field observations
Simulation Governance: An Idea Whose Time Has Come
IACM Expressions, 2015
Dr. Barna Szabó
Chairman and Co-Founder, ESRDAs companies move to digital product development, simulation plays an increasingly important role in supplying information to support product design decisions. Simulation & Analysis (S&A) Governance is a key strategy to manage simulation for maximum effectiveness over the full product lifecycle. Dr. Keith Meintjes, Practice Manager, Simulation and Analysis at CIMdata states “S&A must be recognized as a strategic capability that companies should develop and foster. This extends from the executive suite where the policy is set and supported, through product and manufacturing managers who are the customers for S&A, to simulation practitioners, who are responsible to deliver simulation on time and with quality.” Formal efforts to improve organizational awareness and to improve technical capability need to be put in place to support this vision
CIMdata News
CIMdataEngineering organizations need to institute simulation governance. This means that management has to understand that finite element modeling is not numerical simulation and begin to exercise command and control over all aspects of numerical simulation. This includes adoption of the best available simulation practices, solution verification, data verification, model validation and revision of mathematical models in the light of new information collected from physical experiments. The primary goal of simulation governance is to ensure and enhance the reliability of predictions based on numerical simulation
Many organizations equate the credibility of simulation results with the experience and judgment of their senior analysts. Without diminishing the value of senior analysts, an evidence-based approach to simulation credibility will reduce both the technical risk of producing incorrect simulation results and management’s risk in the use of simulation results in a decision-making context.
Dr. William Oberkampf
NAFEMS Tutor and Engineering ConsultantS&A Governance can help make S&A more predictable, consistent, and productive. Without that consistency, S&A organizations usually lack common methods or shared practices. Consequences include poor re-use of S&A results with its many risks (product failures, increased costs and warranty claims, late to market due to engineering changes, etc.), costly duplication of work, and even the purchase of unneeded systems and solutions. S&A Governance is a strategic way for companies to establish a sustainable competitive advantage in innovation, product quality, and time to market.
Simulation Governance: Managing Simulation as a Strategic Capability
Dr. Keith Meintjes
Executive Consultant, CIMdataVirtual Product Development capability is becoming an asset in many companies. A company’s ability to do virtual validation depends on CAE resources and an ability to do repeatable, reliable and robust CAE at all phases of product development. It is essential that a Governance System be put in place to take advantage of the virtual capability.
2016 NAFEMS Webinar “Simulation Governance: Managing Simulation”
Mr. Ravi Desai
Director, CAE & CAD, American-Axle & ManufacturingThe following are helpful downloads, articles, webinars and references related to Simulation Governance (Sim Gov):
- Planning for Simulation Governance & Management (NAFEMS Benchmark article by Drs. Szabó and Actis).
- Simulation Governance: Technical Requirements (NAFEMS Webinar by Drs. Szabó and Actis)
- The Big Issues in Simulation: Simulation Confidence (NAFEMS Article by Matthew Ladzinski)
- NAFEMS World Congress 2017 Tackles the Big Issues in Simulation and Analysis (DE Article by Jamie Gooch)
- Simulation Governance: Managing Simulation as a Strategic Capability (CIMData Article by Dr. Keith Meintjes)
- A Case for Simulation Governance (DE Article by Dr. Szabó)
- Simulation Governance: New Technical Requirements for Software Tools in Computational Solid Mechanics (October 2011 Presentation by Drs. Szabó and Actis at the International Workshop on Verification and Validation in Computational Science)
- Simulation Governance (Ramsay Maunder Associates)
- Simulation Governance for the Expert Witness (Ramsay Maunder Associates)
- Role of Simulation Governance in Democratization (Comet Solutions Article by Dr. Actis)
- Simulation Governance (Marc 2015 Presentation by Dr. Keith Meintjes at NAFEMS Seminar “”Simulation & Systems Engineering in the Automotive Industry: Emerging Standards & Practices”)
- A System for Simulation Governance of Engineered Repairs of Composite Aircraft Structures (Presentation by ESRD’s Jim Sutton)
- Smart Engineering Simulation Apps (2016 Newsletter by EnginSoft)
- The Role of Simulation Governance in the Democratization of Simulation Through Sim Apps in the A&D Industry (NAFEMS 2017 Presentation by Dr. Actis)
- Simulation Governance: An Idea Whose Time Has Come (IACM Expressions Article by Dr. Szabó)
- Simulation Governance (EnginSoft page)
- The Path Toward Certification by Simulation Part 3: Simulation Governance (Composites World Article by Ginger Gardiner)
- Simulation Governance Wikipedia Article
- Szabó B. and Actis R. Simulation governance: New technical requirements for software tools in computational solid mechanics International Workshop on Verification and Validation in Computational Science University of Notre Dame 17–19 October 2011.
- Szabó B. and Actis R. Simulation governance: Technical requirements for mechanical design. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 249–252 158–168, 2012.
- Meintjes J. Simulation Governance: Managing Simulation as a Strategic Capability. NAFEMS Benchmark Magazine, January 2015.
- Oberkampf WL and Pilch M. Simulation Verification and Validation for Managers. NAFEMS, 2017. ISBN 978-1-910643-33-4.
Consult our Simulation Technology FAQ’s for a summary of how Sim Gov, mathematical modeling and Numerical Simulation are related.
Also, you may review the “Questions Submitted” section in the “Simulation Governance: Technical Requirements” webinar recording page.
Request a Simulation Governance Briefing with Our Team
The application engineers at ESRD have many years of experience helping customers to understand and implement the latest generation of Finite Element Numerical Simulation Software – which is not the same as Finite Element Modelling software – that fully supports the principles and practice of Simulation Governance. If you would like for your engineering team to receive a complimentary private briefing on the lessons learned and best practices of Simulation Governance as applied in the aviation, aerospace and defense industries, send us a request:
Looking for Resources?
Recent News & Events
Quick Links
Testimonials
-
“The p-type element has been used to great advantage in the finite element system ESRD StressCheck, [26]. This software provides the engineer with the means to conduct solution verification in an extremely straightforward manner by simply increasing the degree of the element, monitoring convergence and using Richardson extrapolation reliably to estimate the error. This can be conducted automatically by the software thereby enabling the engineer to concentrate on the engineering rather than the simulation. StressCheck has also been used to develop ESRD’s Handbook and Toolbox applications. The first of these provides engineers with a repository of parameterised standard problems of the type found in texts like Roark’s “Formulas for Stress and Strain”, [27]. The second, Toolbox, is a tool that can be used to parameterise a company’s range of components for rapid and reliable analysis by non-expert analysis. Toolbox then is an exemplary of the way in which the democratisation of simulation can be applied.”
Angus Ramsay, PhD
Engineering Director, Ramsay Maunder Associates
 Serving the Numerical Simulation community since 1989
Serving the Numerical Simulation community since 1989 





